- What is Cauliflower Ear? - July 25, 2013
 Around the mid-1800s, speculations arose regarding the condition of “cauliflower ear.” Some thought it was a symptom of insanity, while others argued that it resulted from the insane hitting themselves, or being struck around the ear by psychiatric staff. The idea that cauliflower ear is related to mental illness has gradually dissipated. We now have proven causes and effective treatments for this condition.
Around the mid-1800s, speculations arose regarding the condition of “cauliflower ear.” Some thought it was a symptom of insanity, while others argued that it resulted from the insane hitting themselves, or being struck around the ear by psychiatric staff. The idea that cauliflower ear is related to mental illness has gradually dissipated. We now have proven causes and effective treatments for this condition.
What is cauliflower ear?
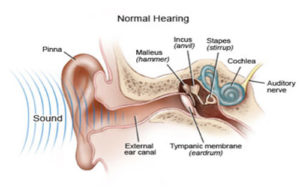
Cauliflower ear is medically known as an auricular hematoma. The external ear is made of cartilage and it is the shape of the cartilage that gives the ear its distinctive shell-like shape. The cartilage is lined by perichondrium, a tight layer of connective tissue.
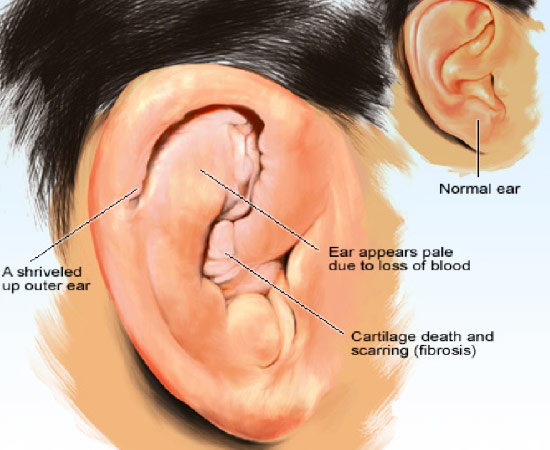
Auricular hematoma/cauliflower ear occurs when the ear cartilage is injured (from a blow or other form of trauma). Trauma results in fluid or blood collecting between the perichondrium and the cartilage. This blood or fluid can become permanent and scarred, resulting in the appearance of cauliflower ear.
What causes cauliflower ear formation?
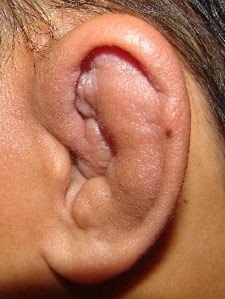
The most common cause of cauliflower ear is a direct hit to the ear. When the cartilage of the ear is injured, it is separated from the perichondrium by blood or fluid from the injury. The collection of blood is called a hematoma. The perichondrium supplies blood and nutrients to the cartilage so when they are separated, the supply of nutrients is disrupted. Because the blood supply is lost, the cartilage is not able to heal easily and instead forms scar tissue. This scar tissue contributes to the swollen and misshapen appearance, thought to resemble a cauliflower.
Who is susceptible to developing cauliflower ear?
- Athletes involved in close-contact sports are the likeliest to develop cauliflower ear. This condition is most common among:
- boxers
- wrestlers
- martial artists
However, auricular hematoma may develop in anyone, after a single blow to the ear.
What are the symptoms of cauliflower ear?
- pain, swelling, or bruising in the affected area
- deformity of the curvature of the ear
- loss of hearing
- ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- pain/tenderness of the ear cartilage
How can cauliflower ear be treated?
As soon as the injury is noted, consultation with a facial plastic surgeon should be undertaken so that the blood may be drained via a small incision in the ear. After drainage, it is important that the perichondrium lie flat on the cartilage again, so that more fluid does not reaccumulate. To reapproximate the skin and the cartilage, a pressure bandage is applied. Antibiotics are often prescribed to prevent or treat infections of the outer ear, or to reduce any inflammation. Cosmetic procedures are also available to improve and refine the ear’s appearance.
How can cauliflower ear be prevented?
To prevent injuries that can cause cauliflower ear, headgear should be worn during close-contact sports. This protective gear will protect the ears, decreasing the risk for injury or trauma. It is crucial that the headgear is of proper fit; a loose helmet can easily slip out of place, and a helmet that is too tight may damage the ears. If one should sustain an injury to the ear, medical evaluation should be sought immediately. Prompt attention by an able physician will decrease the chances of developing cauliflower ear.